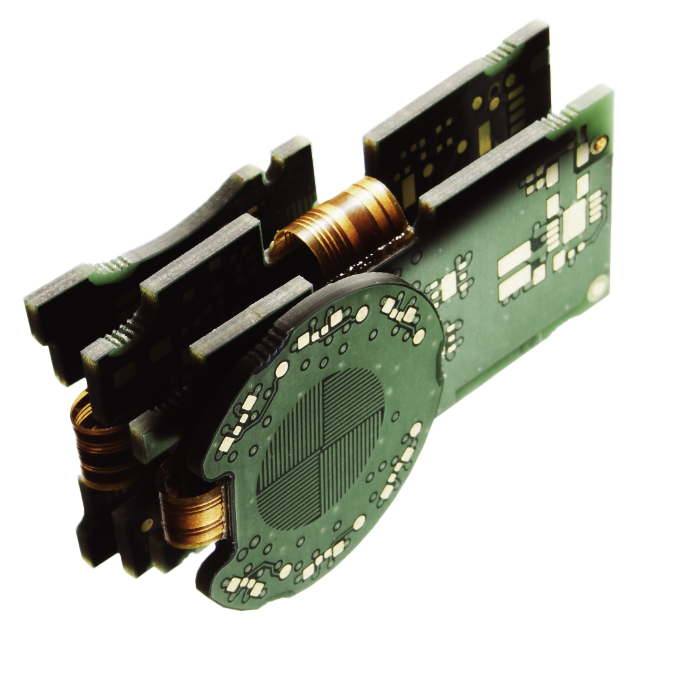
RIGID-FLEX printed circuit boards combine the benefits of flexible and stiff board technologies. These PCBs provide mechanism reliability in condensed packages of extreme conditions that may not be tolerable for connectors. Depending on the application, most rigid-flex boards have some layers of flexible circuit substrates linked to one or more rigid boards externally and/or internally. Flexible substrates are made in a constant state of flex and can be frequently bent into a flexed curve during the complete lifecycle of the product.
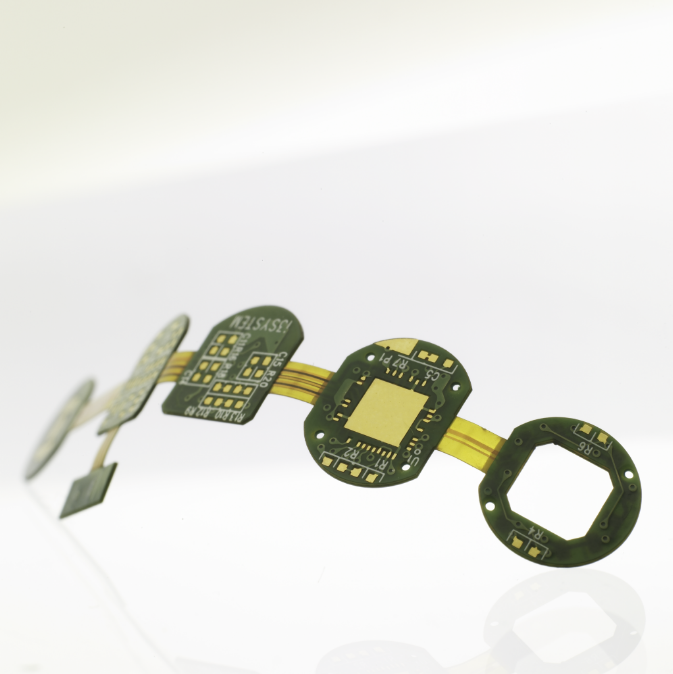

Where are RIGID-FLEX PCBs used?
RIGID-FLEX PCBs offer various applications, ranging from smart devices to cell phones and digital cameras. RIGID-FLEX board fabrication has been increasingly used in medical devices such as pacemakers for their space and weight reduction capabilities. These advantages, together with environmental survivability, make RIGID-FLEX the perfect system for aviation and military guidance systems, weapons, and satellites.
In consumer products, RIGID-FLEX does not just maximize space and weight but significantly improves reliability and improved signal integrity eliminating many needs for solder joints and delicate, fragile wiring prone to connection issues. These are just some examples, but RIGID-FLEX PCBs can be used to benefit nearly all advanced electrical applications, including testing equipment, tools, and automobiles.
RIGID-FLEX printed circuit boards are an excellent solution for assemblies that may be exposed to repeated shock or high vibration. Unlike Rigid Standard PCB, interconnected with cables, they will be reliable in an environment like this. The flex part also resist UV, radiation, harsh chemicals, and oils, ensuring a longer product lifecycle. Although Rigid Standard PCBs are thicker and stronger, RIGID-FLEX systems typically react to unfriendly environments like this more effectively – it may be why these systems are widely used in automotive electronics.